
using Avogadro’s number, using shot noise method etc.\): Periodic Table of Elements that is color coded for atomic mass. Apart from this, there are many other methods to find out the fundamental value of electric charge, e.g.

Protons have a positive electrical charge of one ( + 1) and a mass of 1 atomic mass unit (amu), which is about 1. Repeating the same for different drops, it can be seen that, every time the value of the charge is integral multiple of the elementary charge. This is a tiny, dense region at the center of the atom. An elementary charge is denoted by the letter e and was originated in 1874 by George Stoney. Now we know that electric force on a charge is the product of the charge and the field in which it resides, since we know the field, by dividing the force by the field we can accurately determine the value of the charge in the oil drop. Protons have a charge of +1 elementary charge.
Electric force on it can also be deduced. Proton: The positively charged fundamental particle present in the atom is called proton. Now, the forces on the drop due to gravity and viscosity could be deducted by measuring the speed of the drop and the size of the drop. The forces that would be working on the drop are the gravitational force on it due to its weight, the force due to viscosity as it is falling through air and the electrostatic force on the charges in it due to the electric field.
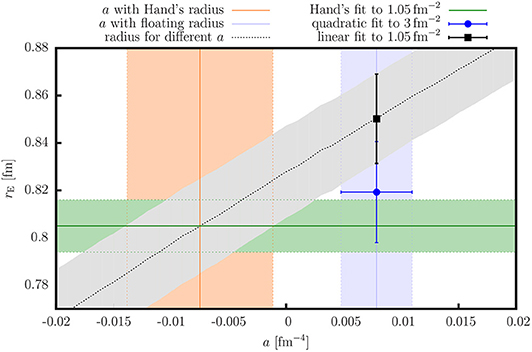
Millikan’s oil drop experiment- In the experiment a small drop of oil was dropped from a height in an electric field. The theory behind the experiment was quite simple and yet brilliant. Thus, to determine the total charge of a. Millikan, through his famous oil drop experiment first measured the fundamental unit of electric charge. The quantity of charge on an object reflects the amount of imbalance between electrons and protons on that object. This is also not a violation of the fundamental unit of charge because quasiparticles are not actually elementary particles. In the quantum Hall effect theory of Robert Laughlin, it is shown that the quasiparticles have fractional charges to that of the elementary charge. The charge is one positive fundamental unit, or 1.602 × 1019 coulomb. On the other hand, quasiparticles are not actually particles but an emergent entity that behaves as particles. The so-called proton charge radius puzzle was one of the challenging problems in physics in the last decade. The +1 represents the polarity and the quantity of the charge the proton carries. Thus, we can justify that our independent fundamental unit of charge is e. But quarks cannot exist in an isolated form. The same number of electrons is required to make 1.00 C of electric charge. The number n of protons required to make +1.00 C is. Hence it can be used the express the charge possessed by any body, not necessarily a proton or electron. Quarks have charge in multiples of 1 3 e \frace 3 1 e. and the electron carries 1.602 × 10 19 C. But there are two cases where it can be thought of as exceptions (but actually they are not). Treating the charges on nitrogen and argon as the sums of charges on protons, electrons and neutrons, it is deduced that the proton charge is (14×1020)e. The corresponding values from the Particle Data Group are and, respectively 8. Elementary charge is basically indivisible. The rms-radius R of the proton charge distribution is a fundamental quantity needed for precision physics. Introduction The question of determining the proton charge radius has regained attention because of the slight, but significant discrepancy seen in experiments using muonic hydrogen 1 4 and experiments using electrons 5 7. It is an important input for bound-state Quantum Electrodynamic (QED) calculations of the hydrogen atomic energy levels. So charges can exist in the form of 0e or 1e or 2e. The electric charge radius of a proton, denoted by, characterizes the spatial distribution of its electric charge carried by the quarks. This principle of any amount of charge being an integral multiple of elementary charge is called Charge quantization. That is the reason behind the terminology, elementary charge. 
It is called the fundamental unit of charge because charge contained in any object is found to be integral multiple of it.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
